Technology has become an indispensable player in the realm of physical security, offering a range of innovative tools and methods to protect people, property, and information from potential threats. Incorporating advanced digital systems and enhancing efficiency, technology improves risk mitigation and helps organizations respond more effectively to security challenges.
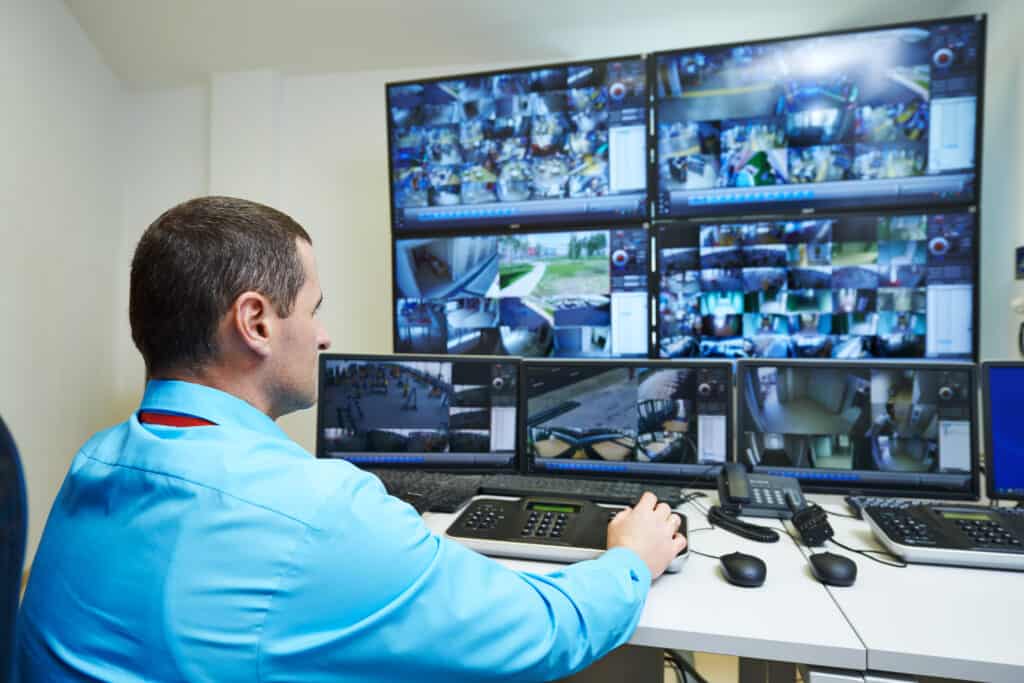
One significant area where technology is making an impact on physical security is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in monitoring and managing various security scenarios. AI-based solutions can better analyze complex data and detect anomalies, leading to quicker identification of potential risks and improved response times.
In addition, technology is vital in enhancing security and safety for travelers in high-risk zones. By providing detailed updates on potential risks and advice on how to navigate in high-risk areas, travelers can be adequately prepared and adapt to situations such as robberies while traveling abroad. The constant evolution of technology continues to enrich the physical security landscape, leading to a safer and more protected environment for everyone.
Access Control and Authentication
In today’s world, enhancing physical security is an integral part of overall cyber security. Access control and authentication play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of personnel, resources, and information.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide multiple forms of identification. This process involves authenticating users based on various factors, such as something they have (e.g., a physical token) or something they know (e.g., a password). Implementing MFA significantly enhances security by adding an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. MFA in access control is particularly useful in situations where hackers attempt to break into systems through brute-force methods or by exploiting weak passwords.
Touchless Security Systems
Touchless security systems offer a novel solution to strengthen access control and minimize risks associated with manual verification methods. These systems utilize technologies like biometric authentication or facial recognition to grant or deny access to restricted areas. In combination with strong physical access controls, touchless security systems offer a more secure and hygienic option for authenticating users in various settings.
Access control and authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication and touchless security systems play a crucial role in improving physical security. Implementing these technologies effectively mitigates risks and ensures the safety of personnel, resources, and information within an organization. Adopting these measures, along with comprehensive threat identification strategies like mail screening, can protect against a wide range of security vulnerabilities.
Video Surveillance and Analytics
Video Analytics
Video surveillance has become an essential tool in maintaining physical security. With the advancement of technology, video analytics has emerged as a powerful solution for detecting incidents and monitoring threats. This technology leverages artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze video data and provide valuable insights to improve security measures and ensure safety in various settings such as hotels, universities, and residential areas.
Not only do video analytics reduce instances of false alarms, they also enhance the overall effectiveness of security systems by recognizing faces and scanning badges for smooth access control protocols, as exemplified by university campuses. Furthermore, the use of video analytics in residential security transforms smart home security by increasing the precision of security cameras in detecting suspicious activities within households.
Intrusion Detection
Intrusion detection is an important aspect of physical security, aiming to identify unauthorized access attempts and potential break-ins. With the integration of video analytics, security systems can efficiently monitor large areas such as hotel lobbies and parking lots, utilizing innovations like panoramic and 360-degree cameras.
In the realm of big data analytics for video surveillance, the constant generation of data from numerous sources serves to increase the potential coverage and scope of security systems. By harnessing the power of technology, organizations can enhance their security processes, respond effectively to incidents, and improve measures for preventing safety breaches.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Proactive vs Reactive Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are playing a crucial role in enhancing physical security. One significant way this is done is by shifting security measures from being reactive to proactive. Proactive security refers to taking steps to prevent incidents before they occur, while reactive security involves responding to incidents after they happen. AI and ML technologies can analyze data, identify patterns of potential threats, and predict future security breaches, enabling security personnel to take preventive actions.
Automation and Efficiency
AI and ML implement automation in physical security systems, improving efficiency and reducing the need for human intervention. Automated systems can continuously monitor an environment, processing vast amounts of data in real-time, and alerting security personnel to potential issues. This level of automation saves time and resources and minimizes the probability of human error in security operations.
AI-based facial recognition systems and advanced threat detection technologies are examples of how automation brings efficiency to physical security. By using AI and ML algorithms, these systems can accurately identify potential threats, making security operations more effective.
AI and ML are transforming physical security by helping shift from reactive to proactive security measures and increasing automation, thus improving the overall efficiency of security operations. The use of these technologies ensures a more secure and safe environment, ultimately benefiting individuals and organizations alike.
Incident Response and Management
Digitalization of Incident Reporting
The digitalization of incident reporting has significantly improved the effectiveness of incident response and management. Digital technologies enable security teams to collect, analyze, and share information more efficiently, helping them identify and prioritize potential threats and hazards. One helpful tool in this process is a THIRA (Threat and Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment), which helps communities evaluate their vulnerabilities and allocate resources effectively.
By using digital incident reporting platforms, organizations can streamline communication, ensuring that all relevant parties receive accurate and timely updates. Additionally, digital systems provide an audit trail, making it easier to review and learn from past incidents and implement necessary improvements.
Crisis Management
Crisis management aims to mitigate the impact of threats on an organization and its stakeholders, focusing on managing the response and recovery from a crisis. Effective crisis management relies on robust planning, communication, and coordination among various parties, including the organization’s security team and external partners, such as law enforcement agencies.
School safety, for instance, is a significant concern that requires proactive crisis management strategies. Implementing safety measures like hard corners and practicing reunification drills can help create safer spaces for students and staff while preparing for potential emergencies.
A crucial aspect of crisis management is maintaining open and effective communication during an incident. Tools like active listening play a vital role in fostering collaboration and understanding the concerns of different stakeholders, improving the overall safety and security of an organization. Technology can facilitate real-time communication and information sharing, enabling security teams to make informed decisions and execute timely responses to incidents.
Integration and Collaboration
The role of technology in enhancing physical security is continuously evolving. A key aspect of this enhancement is the integration and collaboration between various technologies, stakeholder groups, and security professionals. By combining the strengths of different systems and fostering a culture of cooperation, organizations can create a more robust and comprehensive security strategy.
An important aspect of enhancing physical security is the establishment of safety and security teams within specific environments, such as churches. Volunteer safety teams can be an effective and practical solution to address security needs in places of worship, ensuring the well-being of visitors and maintaining a peaceful environment. Creating teams that are integrated with the overall organizational security strategy and collaborating with other stakeholders can significantly increase the effectiveness of security measures.
Moreover, the importance of regular safety and security audits cannot be ignored. For example, in Texas, school safety audits play a critical role in assessing the effectiveness of existing measures and identifying areas for improvement. By understanding the current state of a facility’s safety procedures, administrators can implement necessary changes and upgrades, integrating the latest technology and collaborating with security professionals to ensure a safe and secure environment.
Integration and collaboration are essential to improving physical security through technology. By focusing on the seamless interaction between systems, stakeholder groups, and security professionals, organizations can develop effective strategies that protect people, property, and information more comprehensively.
Emerging Technologies
Drones and Robotics
One of the key emerging technologies in physical security is the use of drones and robotics in monitoring and protection operations. Drones can provide aerial surveillance in large outdoor areas where they can cover wider ground more efficiently than human guards. Robotics, on the other hand, can be employed in various tasks such as patrolling, inspection, and even emergency response, significantly increasing the efficiency of security operations. When combined with advanced sensors and detectors, these technologies can greatly enhance the overall security and surveillance capabilities of organizations.
Edge Computing
Another important emerging trend in physical security is the implementation of edge computing technology. Edge computing offers a decentralized approach to data processing and storage, which can lead to faster response times and improved overall security. By processing data closer to the source, edge devices can help minimize latency and provide real-time insights, ensuring that appropriate actions are taken swiftly.
In the security domain, edge computing can be used to enhance the capabilities of surveillance cameras, sensors, and detectors. For instance, cameras can be equipped with edge computing capabilities, allowing them to analyze the data locally rather than sending it back to a centralized server. This not only reduces the time taken to analyze and respond to potential threats but also lowers the risk of data breaches by minimizing the need for data transmission.
In conclusion, emerging technologies like drones, robotics, and edge computing are playing a crucial role in enhancing physical security. With their ability to improve surveillance, detection, and response capabilities, these technologies are becoming indispensable in addressing the ever-evolving physical security challenges.
Cybersecurity and Physical Security

Vulnerabilities and Mitigation
In today’s digital landscape, organizations face both cybersecurity and physical security threats. Cyber threats can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, disruption of operations, and, in extreme cases, physical harm. Physical security vulnerabilities, on the other hand, may include risks like theft, vandalism, or direct attacks on premises and infrastructure.
To mitigate these various threats, organizations should work towards converging both cybersecurity and physical security elements into an integrated system. A unified security approach not only streamlines the defense process but also enhances the overall security posture. Combining access control mechanisms, surveillance systems, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems helps in creating a comprehensive and robust security infrastructure.
Regulations and Compliance
As technology advances, so do the laws and regulations governing security practices. Governments and industries are constantly updating policies and guidelines to address emerging threats and enhance existing security measures. Adhering to the established regulations and compliance requirements is crucial for any organization aiming to maintain a secure environment.
Some common regulatory frameworks and standards include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data privacy, HIPAA for healthcare providers, and PCI DSS for organizations involved in payment card processing. These regulations not only mandate organizations to implement strong security practices but also hold them accountable for any breach or non-compliance.
In conclusion, organizations should prioritize the integration of cybersecurity and physical security strategies, addressing both vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with the applicable regulations. By doing so, they can prevent unauthorized access, minimize risk, and maintain a secure environment.
Privacy and Data Regulations
In recent years, the role of technology in enhancing physical security has become increasingly important. One aspect that has gained significant attention is the relationship between privacy, data regulations, and security measures. Considering the sensitive nature of certain industries like healthcare, adhering to privacy and data regulations is crucial when implementing technology for physical security.
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) have emerged as a means to accelerate data strategies while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations. They allow companies to gather, analyze, and utilize data while protecting individuals’ privacy and abiding by legal restrictions. As a result, organizations can successfully boost their security measures and minimize disruptions.
Digitalization, the process of transferring paper-based reporting to a digital system, has also been prevalent in increasing the effectiveness of physical security. By integrating various facility technologies, security systems, and risk-mitigation practices, digitalization ensures that organizations remain compliant with privacy policies while enhancing their physical well-being. This modern approach to security is particularly valuable when considering sensitive information in industries such as healthcare.
National policies regarding technology and privacy are also essential in improving physical security. These policies encourage the development of privacy-enhancing technologies while ensuring the rights of individual users. As a result, organizations can foster a safe and secure environment while complying with changing regulations.
Moreover, comprehensive threat assessments play a vital role in maintaining safe and secure spaces, particularly in educational institutions. Implementing a robust threat assessment system assists organizations with identifying and mitigating risks from potential violators of privacy regulations.
Navigating privacy and data regulations is essential for organizations to harness technology in enhancing physical security successfully. By adopting privacy-enhancing technologies, digitalization, and keeping up with national policies, organizations can create secure environments that prioritize both safety and privacy.
Benefits and Challenges
The role of technology in enhancing physical security has both benefits and challenges worth considering. On one hand, it greatly contributes to increased productivity, improved health and safety, and reduced risks for organizations. On the other hand, it can sometimes introduce new challenges that need to be effectively managed to reap the full potential of integrated security systems.
Technology increases productivity by leveraging sophisticated systems in monitoring, managing, and responding to potential security threats. For instance, artificial intelligence can be used to enhance physical safety in the workplace without intruding on daily operations. Furthermore, automation allows for easier compliance with policies and regulations, as well as driving increased efficiency in various aspects of business operations [^1^].
Health and safety benefits are observed by employing advanced surveillance, access control, and alert systems, which provide a safer working environment for employees. For example, computer vision technology can help recognize and label potential hazards in the workplace, facilitating early detection, and response.
However, despite the undeniable benefits, implementing technology in physical security also brings about several challenges. One challenge is the need to constantly adapt to changing conditions and security threats. As technology evolves, physical security leaders must adopt new approaches to stay ahead of potential security risks.
Another challenge is the potentially high cost of implementation and maintenance of new technological solutions, which may strain budgets for some organizations. This often leads to a delicate balance between maintaining affordability and providing optimal security.
Lastly, integrating technology into physical security solutions may also raise privacy concerns among employees and customers, requiring a balance between ensuring safety and protecting individual privacy rights.
In conclusion, the role of technology in enhancing physical security has both significant benefits and challenges. Organizations must carefully weigh the pros and cons, while constantly evolving their security practices in order to maintain a safe and secure working environment.
Future of Physical Security
The physical security industry is embracing new technologies to adapt to evolving conditions and to better protect people, assets, and facilities. The future of physical security is shaped by three significant drivers: advanced analytics, big data, and digitalization.
Advanced analytics helps security professionals make informed decisions by processing and analyzing data to detect patterns and trends. For instance, facial recognition, license plate recognition, and other computer vision technologies can identify potential threats and alert security personnel. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) can prevent incidents by predicting them, thanks to its ability to analyze large volumes of data quickly.
Big data plays a crucial role in the enhancement of physical security by providing insights from various sources, both structured and unstructured, such as social media, weather data, and crowd movements. The integration of big data allows security systems to more effectively identify and respond to potential risks. It also supports real-time monitoring and quick response in case of emergencies.
Digitalization is transforming the physical security landscape by integrating diverse security systems and making them more efficient. Transferring paper-based reporting to digitalized platforms and connecting various facility technologies not only streamlines processes but also reduces disruptions. According to Deloitte, digitalization is an emerging trend that significantly enhances physical security and risk mitigation.
By leveraging these key drivers, the physical security industry is well-prepared to face evolving threats and challenges. The convergence of advanced analytics, big data, and digitalization creates a more proactive and effective security environment, resulting in smarter and safer solutions for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can technology improve access control systems?
Technology can significantly improve access control systems by incorporating features like electronic keycards, biometric scanners, and remote monitoring. These advancements allow for more granular control over who is granted access to specific areas and can also enable real-time tracking of personnel movements within a facility. Moreover, technology can improve overall security by integrating access control systems with other security measures, such as video surveillance and intrusion detection systems.
What are the benefits of using video surveillance in physical security?
Video surveillance plays a crucial role in physical security by providing real-time monitoring and enabling rapid response to incidents. It acts as a visual deterrent against potential criminals and contributes to faster resolution of security breaches. Additionally, the use of advanced technologies like video analytics and facial recognition enhances the overall effectiveness of video surveillance by automating certain tasks and improving the accuracy of incident detection.
How does technology integration enhance security systems?
Technology integration allows different security systems to work together seamlessly, enhancing overall protection. For example, integrating access control with video surveillance enables better monitoring of individuals entering and leaving a facility. Additionally, integrating intrusion detection systems with security cameras can provide a more comprehensive view of potential threats. This holistic approach to security management not only improves response times to incidents but also reduces the likelihood of false alarms.
Can artificial intelligence boost physical security measures?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly boost physical security measures by automating tasks, analyzing large amounts of data, and making intelligent decisions based on that analysis. For instance, AI-powered video analytics can efficiently identify suspicious behavior or unauthorized access, allowing security personnel to focus on other critical tasks. AI can also support predictive analytics, helping organizations identify and mitigate potential security risks before they escalate into more significant threats.
What role do smart devices and IoT play in security management?
Smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) play an increasingly important role in security management by enabling real-time communication and control of security devices. For example, smart locks and alarms can be remotely monitored and controlled via a smartphone or web interface, allowing enhanced flexibility in managing security measures. Also, IoT-enabled sensors can provide valuable data about environmental conditions or potential hazards, contributing to a more comprehensive security strategy.
How do advancements in biometrics enhance physical security?
Advancements in biometrics technology, such as fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris scanners, offer enhanced security by providing a higher level of identity verification than traditional methods like passwords or keycards. Biometric systems reduce the risk of unauthorized access by verifying an individual’s unique physical characteristics, making it more difficult for intruders to gain entry. Moreover, biometric authentication can be combined with other security measures to create a multi-layered protection strategy, further improving overall security.