The Importance of a Church Medical Team
Churches are gathering places for people of all ages and health conditions, making it essential to have a medical response plan in place.
Whether responding to minor injuries or life-threatening emergencies, a trained medical team can provide critical care while awaiting emergency medical services (EMS).
Key Components of Church Medical Team Protocols
1. Establishing the Team
- Recruit Qualified Volunteers: Look for church members with medical backgrounds, such as nurses, EMTs, doctors, or first responders.
- Conduct Background Checks: Ensure all team members pass background screenings to protect the church and congregants.
- Set Clear Roles: Assign specific responsibilities, such as triage, CPR, or communication with EMS.
2. Training and Certification
- CPR and First Aid: All team members should be certified in basic life support (BLS) and first aid.
- Recommended Resource: American Heart Association CPR Certification
- Specialized Training: Consider advanced training for specific needs, such as pediatric CPR or managing bleeding.
- Recommended Resource: Stop the Bleed
- Regular Drills: Schedule practice sessions to keep skills sharp and ensure familiarity with protocols.
3. Creating Response Protocols
- Triage System: Establish a system for assessing and prioritizing medical needs during emergencies.
- Emergency Contact Plans: Keep updated contact lists for local EMS, hospitals, and poison control centers.
- Recommended Resource: CDC Emergency Preparedness and Response
- Incident Reporting: Develop a process for documenting medical events and actions taken.
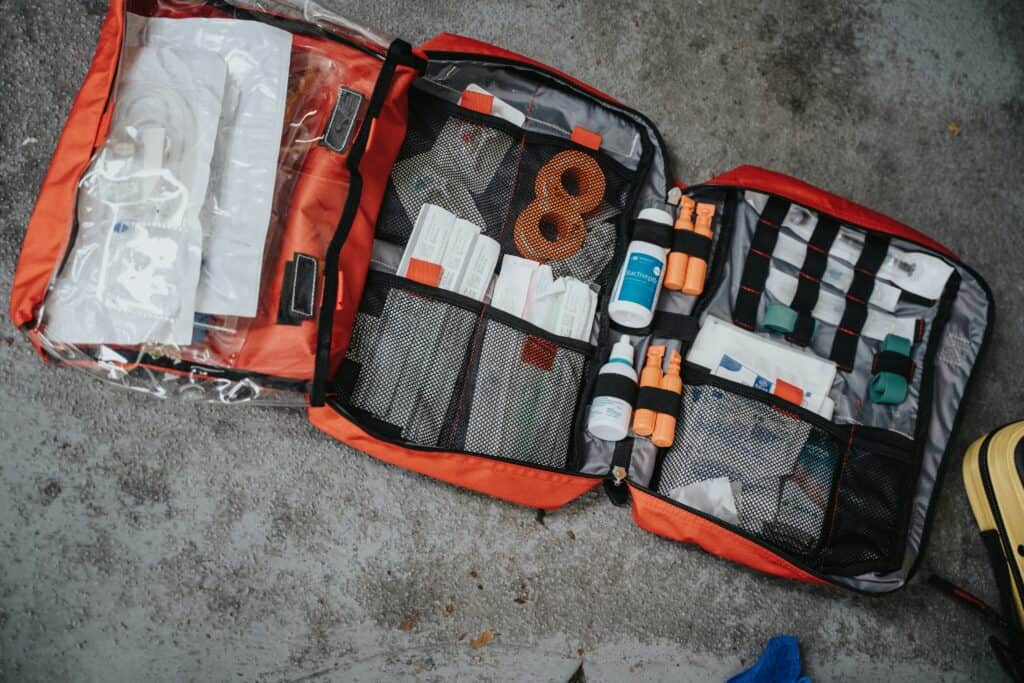
4. Stocking and Maintaining Supplies
- Basic Medical Kits: Include bandages, gloves, splints, and other first-aid essentials.
- Specialized Equipment: Consider items like AEDs (Automated External Defibrillators) and Stop the Bleed kits.
- Maintenance Schedule: Regularly check and restock supplies, ensuring equipment like AEDs is functional.
5. Legal and Insurance Considerations
- Liability Insurance: Verify that the church’s insurance policy covers medical team actions.
- Good Samaritan Laws: Research how state laws protect volunteers providing emergency care.
- Recommended Resource: National Conference of State Legislatures – Good Samaritan Laws
6. Communication and Coordination
- With EMS: Ensure clear communication lines with local emergency services. Provide detailed directions to your church and have a designated meeting area.
- With Congregants: Educate members about how to alert the medical team in an emergency. Use signage or announcements to promote awareness.
Best Practices for Church Medical Teams
1. Customize Protocols for Your Church
Every congregation is unique. Consider factors like building layout, congregation size, and nearby medical resources when designing protocols.
2. Collaborate with Experts
Work with local EMS and healthcare providers to review and improve your plans. Many organizations offer free training and resources to community groups.
3. Regularly Review and Update Protocols
Medical protocols should be reviewed annually or whenever significant changes occur, such as new equipment or team members.
Resources for Churches
- National Safety Council: Offers first aid and emergency response courses.
- Visit NSC
- Stop the Bleed Campaign: Provides kits and training for managing severe bleeding.
- Visit Stop the Bleed
- FEMA Emergency Preparedness Guide for Houses of Worship: Comprehensive planning resources for churches.
- Visit FEMA
Conclusion
A well-organized medical team can make a critical difference during emergencies. By establishing clear protocols, investing in training, and maintaining open communication, churches can create a safe environment for their congregations.
Need help building your church’s safety and medical response plan? Contact us for consultation and training.
Disclaimer
This article provides general information about creating church medical team protocols. It is not intended as legal, medical, or professional advice. Churches should consult licensed medical professionals, legal counsel, and insurance providers to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.