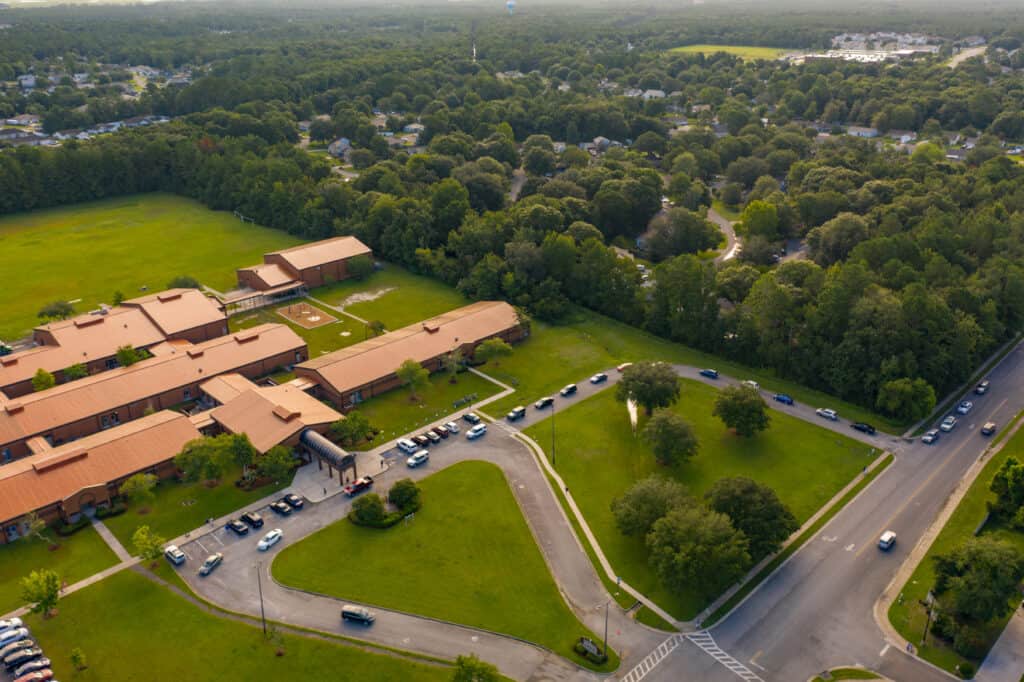
Portable instructional buildings have become an essential part of many educational institutions, providing additional classroom space and flexibility.
Ensuring safety within these structures is extremely important, as outlined in the resource developed by the 86th Texas Legislature SB 11.
The resource highlights best practices, which are actions or techniques believed to be effective in achieving safety goals.
Schools should consider their specific needs, resources, and other factors when determining the most appropriate practices to adopt.
The best practices for safety in portable instructional buildings are organized into several functions, such as access control, communication, structural protection, access and functional needs, surveillance and monitoring, drills and response, and safety procedures.
Access control is a significant challenge for school facilities and focuses on the selective restriction of access to buildings and resources.
Implementing appropriate locking systems, fencing, and gates can help maintain secure access to portable buildings while remaining compliant with local building codes and ADA requirements.
Additionally, a facility security plan and protocols should be in place to ensure efficiency in maintaining safety standards.
Best Practices Overview
The importance of implementing best practices for safety in portable instructional buildings cannot be overstated, as the Texas Education Code requires schools to ensure student safety and the safety of all persons in such structures.
In response to the state legislation, the Texas Education Agency (TEA) worked in conjunction with the Texas School Safety Center (TXSSC) to offer guidance and support for implementing best practices that comply with Senate Bill 11 (SB 11).
To address the various aspects of school safety, these best practices can be grouped into seven primary categories:
- Access Control
- Communication
- Structural Protection
- Access and Functional Needs
- Surveillance and Monitoring
- Drills and Response
- Safety Procedures.
Considering the unique characteristics of portable instructional buildings and the specific needs of each school district, the implementation choices of these practices can be tailored to maximize their effectiveness.
However, it should be noted that the practices mentioned comply with the federal and state legal requirements and have reportedly been proven through research-based practices and experience.
Access control is crucial in managing the selective restriction of access into and out of portable instructional buildings.
A variety of methods can be used, such as exterior door locks, fencing, and gates, to ensure a secure environment through authorized entry points for students, staff, and visitors, while staying compliant with ADA requirements.
Effective communication is equally important, as it facilitates proper coordination between Local Education Agencies (LEAs), law enforcement, first responders, and emergency services in the event of any security concerns or emergencies.
Having a clear and streamlined communication system in place ensures the efficient protection of all individuals in the school setting.
Structural protection encompasses measures to strengthen the physical security of portable buildings while taking into account each facility’s unique features.
Access and functional needs must be considered to ensure these structures remain accessible and compliant with local building codes and Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements.
Surveillance and monitoring, too, play a key role in maintaining the safety of portable instructional buildings.
By installing security cameras and other monitoring systems, schools can proactively deter potential threats and monitor any unusual activities happening within their premises.
Additionally, regular drills and response exercises are essential to prepare staff (including substitutes) and students for various emergencies.
This practice builds familiarity with established procedures, ensuring a faster and more efficient response to potential emergencies.
Finally, schools need to adopt clear and comprehensive safety procedures, which include threat assessment teams, mental health promotion programs, safe and supportive school programs, and guidelines regarding compliance with state laws such as SB 11.
Adherence to these policies and procedures can help create a safe environment, prevent potential threats, and support the well-being of all individuals within the portable instructional buildings.
Overall, addressing these key areas with the best practices compiled by the Texas School Safety Center and TEA, and keeping in consideration the unique needs of each public school or school district, can significantly contribute to creating a safe and secure environment for all individuals in portable instructional buildings.
Access Control
Good access control is vital for ensuring security in portable instructional buildings.
Access control refers to the selective restriction of access to a place or resource utilizing various measures, such as door locks, fencing, and gates.
Access control can help maintain safety and security in portable instructional buildings by adhering to approved building standards and facilities standards, as well as considering the design, construction, renovation, or retrofitting of such structures.
Exterior Door Locks
Appropriate door-locking systems are crucial for restricting unauthorized access to portable instructional buildings.
This may include key locks, magnetic locks, or electronic locks, to list a few.
Portable classrooms or temporary structures should have locking systems that secure all doors to the building and allow occupants to secure themselves from the inside.
When selecting and installing door locks, it is important to comply with local building codes, fire codes, and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements.
Fencing
The strategic implementation of proper fencing can effectively restrict access to portable instructional buildings and designated areas.
Fencing should be designed to limit direct access to portables from parking spaces, roadways, or other school property.
The appropriate choice of fencing types, height, and location will depend on the specific functional needs and protocols of the facility as well as state and/or federal requirements.
Gates
Gates can serve as an essential component of access control when used in conjunction with fencing.
They allow for secured entry to portable instructional buildings, whether monitored by personnel or electronic means.
Gates should be designed and placed according to the facility’s security plans and protocols.
The selection of gate types, locations, and features should be dictated by the functional requirements of the facility in question.
By following these best practices for access control, schools can ensure a higher level of safety and security for students and staff in their portable instructional buildings.
Communication
In the context of portable classrooms and temporary structures, the importance of effective communication cannot be overstated due to the unique challenges these environments present.
Ensuring reliable and audible communication in such settings is not just a best practice; it is a necessity for the safety and security of students, staff, and visitors.
Access to communication devices is paramount.
Every portable classroom must be equipped with telephones, cell phones, or other electronic communication devices to facilitate immediate contact with emergency services or responders.
This requirement aligns not only with best practices but also with legislative mandates, such as SB 11 and TEC 37.108, emphasizing the critical nature of such provisions in emergencies.
To ensure the effectiveness of these communication tools, periodic testing of signal strength in and around the portable structures is advised.
This proactive approach guarantees that communication lines remain functional at all times, especially in scenarios where swift response is crucial.
In addition to the availability of communication devices, the audibility of communications plays a significant role.
Warnings and announcements must be audible not just within the portable classrooms but also in the surrounding outdoor areas.
This is particularly important for those moving between buildings or participating in activities near the portables.
By ensuring that vital information can be heard clearly in these areas, schools can effectively manage safety protocols and respond to emergencies more efficiently.
Overall, the implementation of these communication strategies in portable classrooms and temporary structures is fundamental to maintaining a safe and secure educational environment.
By providing accessible communication devices and focusing on the audibility of important announcements and warnings, schools can better prepare for and respond to emergencies, ensuring the well-being of everyone on campus.
Structural Protection
In addressing the challenges associated with portable classrooms, particularly their inherent limitations in protecting from natural, technological, or manmade hazards compared to permanent structures, a focus on structural protection is paramount.
These best practices for mitigation are crucial for creating a safer environment for students and staff.
Compliance with local building and fire codes is a foundational aspect of ensuring the safety of portable classrooms.
These structures must adhere strictly to jurisdictional regulations to maintain structural integrity and safety standards.
This adherence not only guarantees the basic safety requirements but also serves as a proactive measure against potential hazards.
With that in mind, another key aspect is the proper skirting and underpinning of portable buildings.
Adhering to building codes in this regard, portables should be underpinned effectively to support stability and durability.
Additionally, the space between the ground and the portable floor should be skirted with suitable materials.
This practice not only prevents unauthorized access beneath the structure by people or animals but also protects vital utility connections like water and gas lines from tampering or damage.
Additionally, during the placement, installation, use, maintenance, and removal of these portable buildings, it’s essential to ensure that utilities are safeguarded from vehicle damage.
The structural integrity of portable classrooms extends to the consideration of doors and their surrounding areas.
Steel doors with steel frames are recommended over hollow core doors for exterior use, owing to their enhanced durability and security.
This choice significantly reduces the risk of breaching.
In conjunction with secure doors, reinforcing the exterior walls surrounding these entry points is an important measure.
Such reinforcement can greatly enhance the building’s resilience against potential break-ins or other security breaches.
In essence, the structural protection of portable classrooms involves a comprehensive approach.
From strict adherence to building and fire codes, through effective skirting and underpinning, to the reinforcement of doors and surrounding structures, each element plays a vital role in mitigating the risks associated with these non-permanent educational spaces.
Access and Functional Needs
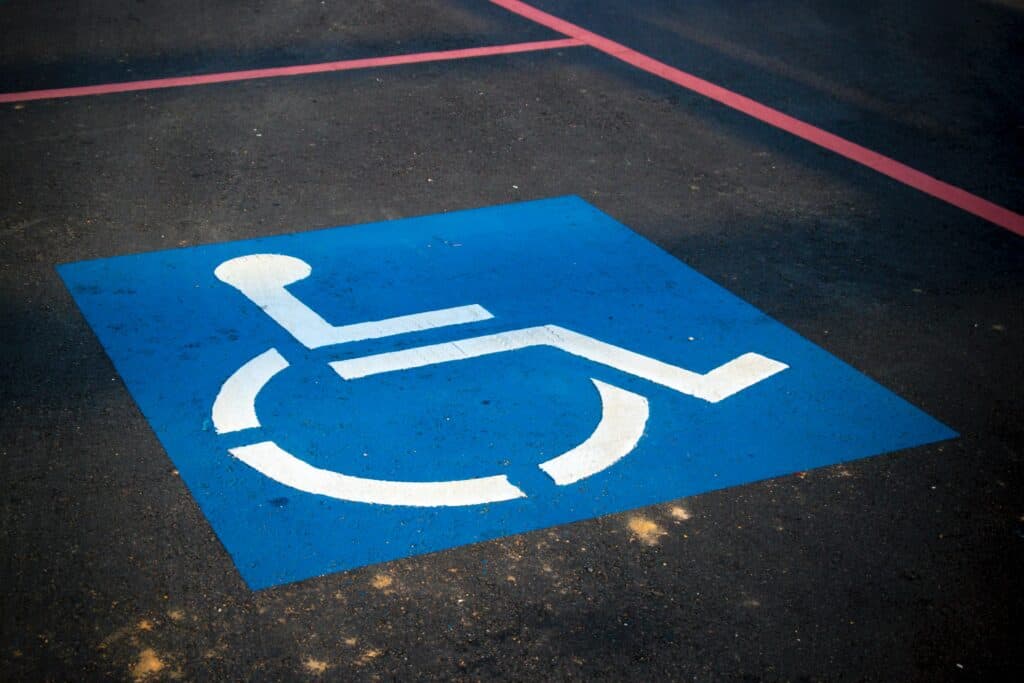

Access and functional needs refer to the requirements of individuals with disabilities or special needs to have equal access to facilities, programs, and services within a school setting.
Implementing appropriate considerations for students and staff with access and functional needs in portable instructional buildings promotes an inclusive environment and ensures the safety of all.
1. Accessible Entrances and Routes: Portable instructional buildings should include accessible entrance ramps or pathways for students who may require the use of wheelchairs, walkers, or other mobility aids. These routes should comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards, be well-maintained, and be kept clear of obstructions.
2. Accommodation in Special Programs: Special education programs or other special programs within portable buildings should have adequate space and equipment needed to cater to the specific needs of students participating in these programs. This may include specialized furniture, adaptive equipment, or additional resources to support their learning and engagement in school activities.
3. Communication Systems: Incorporating effective communication systems, such as visual and auditory alarms, ensures that students with sensory impairments receive necessary information during emergencies or drills. The use of appropriate signage, technology, or visual aids can also help students navigate the portable instructional buildings effectively.
4. Emergency Evacuation Plans: Portable instructional buildings should have established evacuation plans that consider the unique access and functional needs of students and staff. This may involve designated safe areas for individuals with mobility impairments or specialized training for staff responsible for assisting students during an emergency.
5. Collaboration with Support Staff: Teachers and other staff within portable instructional buildings should work closely with special education professionals, therapists, and other support staff to identify and address the needs of students with access and functional needs. Regular communication and collaboration ensure that accommodations are implemented effectively and consistently across the school environment.
To ensure inclusivity and accessibility in portable instructional buildings, it is vital to consider the access and functional needs of all individuals.
Portable classrooms must be equipped with ADA-compliant ramps or pathways, catering to the needs of those who use wheelchairs, walkers, or other mobility aids.
Emergency exits should also be accessible to everyone, with clear signage indicating routes and exits that are not to be used during emergencies.
These modifications should be thoughtfully integrated into the design and layout of the portable structures, ensuring equal access to safety for every individual in emergencies.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Effective surveillance and monitoring play a crucial role in maintaining the security of portable instructional buildings.
Let’s take a look at surveillance and monitoring best practices in the context of school safety.
Camera Systems: The strategic placement of video cameras within and around portable instructional buildings allows for continuous monitoring and recording of activities. This may include areas such as entrances, exits, and hallways. A combination of both visible and discreet cameras can act as a deterrent to potential intruders or individuals with malicious intent.
Alarm Systems: Intrusion alarm systems, when properly installed and maintained, can support the overall security of portable facilities. These systems detect breaches and unauthorized access points, promptly notifying designated personnel or even local law enforcement. It is important to allocate sufficient funding to ensure the utilization of advanced alarm systems as part of the school’s security plan.
Access Monitoring: Employing an electronic access control system can help track and regulate the entry of people into the portable instructional buildings. This includes the use of key cards, personal identification numbers (PINs), or biometric access systems. By collecting data on individuals entering and exiting the facilities, a school can conduct ongoing security assessments and strategic allocations of funding.
Regular Inspections: In addition to electronic surveillance and monitoring, regular security inspections should be conducted to assess the overall safety and compliance of the portable instructional buildings. School staff can check for possible vulnerabilities, such as unsecured doors, windows, or fencing, and address these issues promptly to maintain the safety of the school community.
Training and Coordination: Staff members should be trained in monitoring and security protocols. This includes understanding the use of surveillance equipment and identifying potential threats. Additionally, maintaining open lines of communication with local law enforcement and first responders promotes a coordinated response to any potential security incidents.
Implementing effective surveillance and monitoring systems is crucial for the security of portable instructional buildings.
This includes installing video cameras around key areas such as entrances, exits, and hallways for continuous monitoring.
These cameras should be a mix of visible and discreet to deter potential threats.
Additionally, well-placed lighting around these structures can help prevent criminal activity and enhance safety, especially during early morning and evening hours.
Regular checks and maintenance of these systems ensure their optimal functioning, contributing significantly to the overall security of the portable environment.
Drills and Response
Schools should implement regular drills and response plans to effectively handle various threats and emergencies.
By engaging in routine training and preparation, school staff, students, and first responders can improve coordination and communication during an actual emergency.
Safety Procedures: Establishing clear safety procedures for various emergency scenarios is crucial to ensuring a secure environment for students, teachers, and staff. These procedures should include evacuation routes, lockdown protocols, and a designated assembly area. Schools should also consider investing in safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers, first aid/trauma kits, and communication devices.
Drills: Conducting periodic drills can help students, faculty, and staff become familiar with safety procedures and respond effectively during an emergency. Examples of drills include fire drills, lockdown drills, and severe weather drills, to name a few. In Texas, the frequency of drills should comply with the Texas School Safety Center guidelines.
Threat Prevention: Efforts to prevent threats should include collaboration between school administration, teachers, students, and first responders. Encourage the identification and reporting of any suspicious behavior or potential threats. Schools can also implement threat assessment and management practices, such as behavioral monitoring and case management.
Emergency Services and First Responders: Establishing a strong relationship with emergency responders, such as law enforcement, fire departments, and medical services, is crucial for an effective response during an emergency. Schools should share their response plans and drill schedules with these entities, ensuring they are familiar with the school’s layout, procedures, and unique challenges associated with portable classrooms.
Conducting regular drills and establishing clear response plans are essential for preparing students and staff for various emergencies.
Drills should include scenarios like fire, lockdowns, and severe weather to list a few, ensuring familiarity with evacuation routes and safety procedures.
Portable classrooms may require specific considerations in these drills, such as different evacuation criteria or protocols due to their unique structure and location.
Collaboration with local emergency services in these drills can provide valuable insights into improving emergency responses and ensuring the safety of everyone in portable instructional buildings.
Safety Procedures
Safety procedures play a vital role in maintaining a secure environment for students and staff in portable instructional buildings.
These procedures encompass various aspects, such as drills and response, bleeding control stations, and collaboration between stakeholders.
Implementing appropriate safety procedures ensures adherence to school safety standards and multi-hazard emergency operations plans.
Regular drills and response activities must be conducted to familiarize students and staff with emergency scenarios.
These drills should follow the multi-hazard emergency operations plan guidelines, covering incidents like fire, severe weather, intruders, and potential violence.
An effective response plan should include predetermined roles for all staff members and communication channels during emergencies.
Bleeding control stations should be strategically placed throughout the portable instructional buildings, providing immediate access to essential supplies in the event of life-threatening injuries.
These stations must be equipped with appropriate supplies, such as tourniquets, pressure dressings, and gauze.
Staff members should be trained to utilize these supplies efficiently and confidently during emergencies.
Establishing a memorandum of understanding (MOU) between schools and various stakeholders, such as law enforcement agencies, emergency responders, and healthcare providers, is essential.
This collaborative approach paves the way for effective communication and resource sharing, ensuring a coordinated response during emergencies.
Schools must adhere to these guidelines, incorporating them into their security and safety plans, while also providing transparent feedback to ensure continual improvement.
Following school safety standards not only enhances the overall security structure but also contributes to a positive learning environment.
School administrators and staff should remain proactive in identifying potential risks and implementing solutions per these standards.
A comprehensive multi-hazard emergency operations plan should be in place, addressing various types of emergencies relevant to the portable instructional building setting.
This plan must outline the roles and responsibilities of staff, communication protocols during emergencies, and evacuation routes, facilitating a coordinated response.
Finally, the incorporation of grief and trauma-informed practices in safety procedures is crucial for the emotional well-being of students and staff during and after crises.
Comprehensive safety procedures are key to creating a secure environment in portable instructional buildings.
This includes the implementation of visitor management procedures, ensuring all visitors pass through an authorization process and possibly escorted to the portables.
Finally, procedures for student safety when traveling between portable classrooms and the main school building should be established.
These should consider adult supervision and the safest routes for students to travel. In emergencies, ensuring that first responders have clear access to the portable classrooms is crucial.
This may involve installing emergency access gates or using materials in fences that can be easily breached by emergency services if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
What safety measures should be integrated into portable instructional buildings for effective access control?
To ensure effective access control in portable instructional buildings, it is important to implement measures such as exterior door locks, fencing, and gates. Building/facility doors should have appropriate locking systems, including key locks, and magnetic, or electronic locks. Portable classrooms should have locking systems that secure all doors and allow occupants to secure themselves from the inside. Fencing should be strategically placed to restrict access to buildings and areas, while gates should be used in conjunction with fencing for secured entry.
How can schools ensure reliable communication channels in and around portable classrooms?
Reliable communication channels are crucial for the effective functioning and safety of portable classrooms. Schools should invest in a robust communication system that integrates portable classrooms with the main school building, ensuring seamless information flow between teachers, administrators, and students. Consider utilizing communication tools, such as intercoms, two-way radios, or emergency notification systems to maintain clear, timely, and consistent communication across campus.
What are the structural protection best practices for portable classrooms in various hazard scenarios?
To safeguard portable classrooms in different hazard scenarios, schools should adhere to structural protection best practices, such as:
- Ensuring compliance with local building codes and standards for portable structures.
- Conducting regular inspections and maintenance of portable classrooms, addressing any areas of concern or potential hazards.
- Considering location-based risks, such as potential flood zones or regions prone to high winds, when installing portable classrooms. Seek guidance from professional engineers who can assess and recommend adequate structural protection measures.
In what ways can accessibility for individuals with functional needs be accommodated in portable instructional buildings?
Accessibility in portable instructional buildings can be accommodated by implementing features that comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requirements. Some of these include ramps, wider doorways, modified restrooms, and visible and audible alarms for emergency notifications. Planning and designing the layout of portable classrooms to accommodate wheelchair users and ensuring easy navigation for individuals with functional needs is vital.
What surveillance and monitoring strategies are recommended for maintaining safety around portable classrooms?
Surveillance and monitoring strategies in and around portable classrooms should aim to achieve a balance between security and privacy. Consider installing security cameras at strategic locations with proper signage informing the presence of surveillance systems. Periodic security patrols by designated staff members or security personnel can also contribute to maintaining a safe environment. Furthermore, it is essential to monitor and regularly review the footage to identify potential safety threats or issues requiring intervention.
How should emergency drills and response plans be adapted for portable instructional buildings?
Emergency drills and response plans for portable instructional buildings should be developed considering the unique nature of these structures and their connection to the main school building. Adapt and customize drills for different emergency scenarios, such as lockdowns or evacuations, taking into account routes, accessibility, and procedures specific to portable classrooms. Ensure comprehensive training for students, teachers, and staff members and schedule regular drills to maintain preparedness and familiarity with emergency protocols in these settings.